Technology is the instrument used to initiate community growth through creative innovations under coworking spaces known as Tech Hubs. They are the ‘salt of the earth’ to finding solutions for societal growth and development.
As oxygen is to humans in respiration, so are tech innovations to the 21st-century new millennium. The global community is made into a close-knit village thanks to the advanced level of technology continuously modified with updated versions to make life and work easier.
A Tech hub is a place where technology, talent, inventors, educators, and startup companies can thrive, whilst contributing to a larger tech ecosystem that creates solutions for everyday problems using technology as a tool.
In other words, Tech Innovation Hubs are simply platforms comprising start-up firms concentrated or localized in a region to add to the economic prosperity of the community. The difference is usually country miles apart when the comparison is drawn between a place that is potent with tech hubs therein and another place that lacks it.
Since the emergence of Tech Innovation Hubs in many countries around the world, they have brought about a new dimensional approach towards the concept of problem-solving and development of new startups coupled with incubators and accelerators contributing to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of economies. This was a result of the increase in growth of new startups and expansion of the economic base to new tech innovations providing coworking spaces to increase the efficiency of labor.
AFRICA IN PERSPECTIVE
The African continent is yet to fully key into these new vistas of creative tech innovation hubs to utilize its human and natural resources constantly brain-drained to Western and other developed countries providing the platforms for their growth and development.
However, in recent developments, the G20 is set to incorporate the African Union as part of its members as first proposed by American Economist Jeffrey Sachs in 2020. When this happens, it means countries of the African continent will be systemically represented and benefit from their developmental policies – including innovations through tech hubs that have driven economies of member countries and other problem-solving abilities for the developing countries in the continent.
Out of the 442 active tech hubs in Africa, Nigeria houses 90 of them according to Statista, making it the largest in the continent.
Tech hubs give birth to start-ups. Currently, the ranking of startups based on quantity and capacity in some of Africa’s commercial cities are:
Lagos – 8.38 points
Capetown – 5.17 points
Johannesburg – 4.94 points
Cairo – 4.9 points
Nairobi – 4.82 points
As apparent from the figures above, Lagos takes the lead in the number of increasing startups.
South African cities occupy the last two spots in Capetown and Johannesburg, just enough to put the country on the map with two major commercial cities.
Cairo follows next with almost half the number in Lagos. Kenya’s capital Nairobi is the only city from East Africa trailing the one from the Northern part with just a few numbers.
Nonetheless, in the past decade, Africa has witnessed significant growth and the establishment of some tech innovation hubs in the continent.
Nigeria is the most populous and largest economy in Africa. With a population of over 206 million (of which up to 70% are based in rural areas), it has more than 750 startups as tech hubs continue to grow across the country. The Nigerian tech industry is deeply rooted in the southwest region of the country (Lagos in particular) with 55% therein.
ROLES AND FUNCTIONS OF TECH INNOVATION HUBS IN THE SOCIETY
Tech Innovation Hubs play many roles in the cities and communities they exist. But some significant functions they carry out are spelled out below:
Stimulating Growth of Start-ups: The existence of tech hubs leads to the development of start-ups in areas of their operation due to the innovative and creative mindset using technology to stimulate the growth and development of new ideas for problem-solving.
Problem-Solving: One of the major roles tech hubs play in the economy is the identification of problems and coming up with a sustainable and efficient way of addressing them driven by technology to add value to human lives and the community at large.
Training/Discovery/Development of Talents: Human capital development in form of talents and skills is imperative to societal development. Tech hubs are platforms that refine and polish talented minds with sound tech knowledge to help them navigate the tech circle and explore a wide range of possibilities to solve problems and innovate tools to that effect.
Capital: Tech hubs also provide investment and funding to finance new ideas for start-ups to flourish. This could be narrowed down to the creation of employment through the multiplier effect at the grassroots.
Research: In the quest to make life easier and also solve problems, research is needed and tech hubs are centers that engage and invest in massive research to provide new modifications of doing things through technology and innovative methods to reflect the change in times and dimensions from the challenges we are confronted.
Advancement of the Economy: Just like Small and Medium Scale Enterprises are fundamental to the development of any economy, so do the tech hubs play key roles in advancing economic growth and development. No surprise some of the world’s leading economies are tech-driven with substantial hubs spread across regions.
Co-working spaces: The tech hubs liaise and network with start-ups and regulatory stakeholders in the economy to ensure the smooth running of a tech innovative atmosphere for thriving. Plus, providing a convenient coworking space for networking between human resources, brainstorming and a working environment that feels like home with some features to bring the best out of workers that coexist therein.
NORTHERN NIGERIA AND TECH INNOVATION HUBS
The Northern part of Nigeria consists of 19 States. Altogether, the region is the most populous in the country. Unfortunately, it has not translated well in their economic prosperity as the same region is the most plagued with poverty in Nigeria. Needless to say, apart from basic infrastructure that is a deficit in many states, there are inadequate tech hubs to identify and solve some of these problems the government can’t do alone. Therefore, the ability of the Northern Nigerian States to provide an enabling environment to these investors will bridge the gap between the numbers of tech hub present when compared to the Southwest region with the highest numbers.
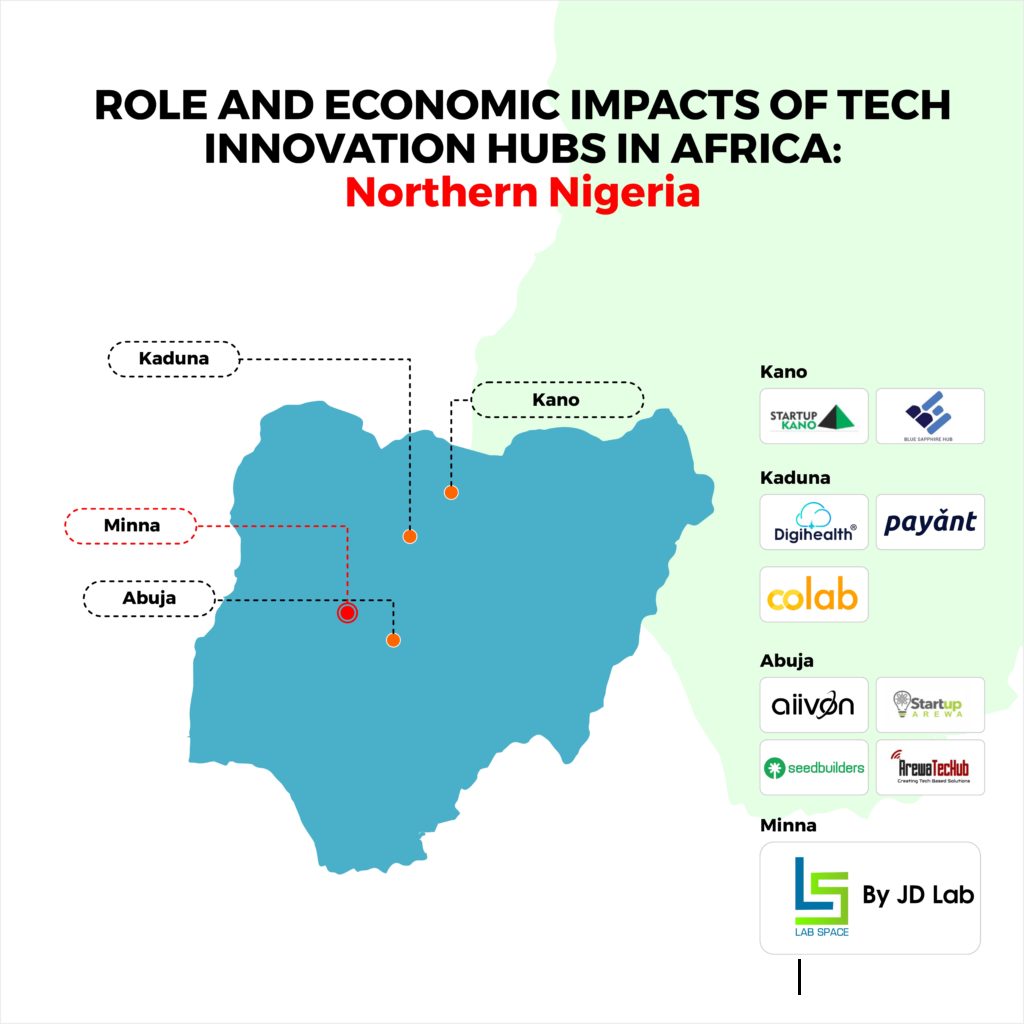
It is noteworthy to mention taking a look at the top three States in Northern Nigeria with a reasonable number of tech hubs present and the impacts they make.
KADUNA
Kaduna is usually referred to as the capital of Northern Nigeria. But until recently, it has failed to live up to that name in the past. With the emergence of Mall. Nasir El-Rufai as the Governor of the State, the tides were turned around as it reclaimed back the honor after it took over Kano as the State with the highest Internally Generated Revenue (IGR) in Northern Nigeria.
This didn’t happen by accident as there was a blueprint to attract investors from around the world to cast their nets in Kaduna. The creation of the Kaduna Investment Promotion Agency (KADIPA) was a pragmatic initiative that brought about an increase in investment and tech hubs driving the economy of the State. Some examples of startups flourishing under tech hubs in Kaduna are:
Payant: a Payment-processing startup by Aminu Bakori in 2017. By 2018, it had processed over 1 billion Naira in transactions. Other subsidiaries of it are MyFlex and Dot. Payment Services.
Digi Health: Founded in 2019 by Emmanuel Bala Musa and Andrew Thomas Kantiok, Digi Health is a health start-up for doctors in terms of mobility and ease of movement for service delivery. By November 2020, it had about 100 clients and 15 medical doctors on board.
KANO
Kano is known as the center of commerce and is also famous for being the most populous state in Nigeria. For it is still the heart of business in Northern Nigeria. But for a State of its stature, it is lagging behind in terms of adopting technology to drive the economy. Business transactions are yet to be widely digitalized. Hence, the need for more tech innovation hubs to be set up to augment the few that exist for its growing population.
Blue Sapphire Hub: this creation is very important because it was founded by a woman – Maryam Lawan Gwadabe, who piloted the first female-owned innovation hub in Northern Nigeria. It went on to produce 12 tech-driven start-ups and created 3,000 jobs in the process.
Startup Kano: is also another hub in Kano that serves as an incubator and accelerator for training entrepreneurs to secure investment from public and private sectors.
ABUJA
Being the capital of the nation means naturally, the city will attract more Hubs than any other place in Nigeria. So in this context, the city is mentioned because it happens to be within the northern zone of the country. Many tech hubs in different parts of the country have gone to open/mark their presence in Abuja to expand and broaden the scope of their operation to cover the country. In a recent report by Disrupt Africa on Nigerian Ecosystem 2022, it was revealed that Abuja is a new home for hubs in Nigeria and hosts the likes of Seedbuilders Innovation Hub, Aiivon Innovation Hub, Ventures Park, Work AND Connect, Startup Arewa and many more.
Seedbuilders Innovation Hub: Seedbuilders Innovation Hub is a Launchpad and Accelerator for Startups and Social Projects, a Digital Knowledge Transfer Center, and a Technology and Research Startup Support Hub with a thriving coworking community.
Seedbuilders Innovation Hub has supported over 30 startups through hackathons and accelerator programs especially female-led startups in Nigeria.
Seedbuilders is bridging the digital divide by training over 1,000 individuals in Nigeria on contemporary digital skills to connect startups and tech companies to readily available and equipped talent to help them scale quickly.
As a change maker, Seedbuilders has held several conferences partnering with several different stakeholders in the technology and creative ecosystem to build a more robust, inclusive, and collaborative industry through programs such as the Startup Week series in Abuja.
Aiivon Innovation Hub: is a tech hub located in Wuse, Abuja. It has been building capacity for startups for 6 years and has supported over 60 startups through a focus on research and development, consultancy, incubation program, and mentorship.
Venture Park: this is a curated coworking space located in Maitama, Abuja for entrepreneurs and brilliant minds to share common interests and goals – to express their creativity. It is equipped with high-speed Internet, front office services, a gym, and artsy finishes to enjoy working.
Work and Connect: sited in Jabi, Abuja, Work, and Connect offer a coworking space to meet interesting and innovative young Nigerians, and training halls for hosting educational activities among other services.
Startup Arewa: founded on the core values of Innovation, Credibility, and Development, Startup Arewa is a tech ecosystem that stimulates entrepreneurship for economic growth. It also develops programs that equip and empower entrepreneurs and innovators to share resources. It is located in Kado, Abuja.
Arewa Tech Hub: this is another tech hub in Maitama, Abuja which serves as an innovation centre for bridging the technological gap in Northern Nigeria. It aims to do that by leveraging social capital for economic growth by devoting considerable time and effort to helping entrepreneurs succeed through the provision of funding, business advisory, and valuable relationships.
MINNA IN FOCUS
Minna is one of the closest cities to the nation’s capital—Abuja. But it is still a budding ground awaiting investments. As the capital of Niger State, it happens to be one of the few cities in the State with tech innovative hubs available to help profer tech solutions to community problems.
JD LAB: is a prominent tech hub in the city with a presence in Abuja, JD LAB is one of the newest members of AfriLabs hubs and network. Over the years it has grown to be an active solution provider in the educational sector, community development, creation of jobs, training, and development of human resources, and contributor towards economic growth and development of Niger State through its tech-driven innovations. JD LAB is currently led by its founder and CEO Abdulkadir Suleiman Lapai, Abdulkadir recently revealed how JD Lab was recently spotlighted by stamp.ng and how the company participated in an accelerator program by Founder Institute with her ed-tech startup called Tespire LLC, while the ed-tech startup is currently in its early stages and closing out its pre-seed round in fundraising. In the past, JD Lab has supported community events like the first-ever TEDx event in Minna and Niger State.
Other tech hubs in the state are the Minna Institute of Technology and Innovation (MITI) and Paritie Innovation Hub amongst others.
ECONOMIC IMPACTS OF TECH AND INNOVATION HUBS IN MINNA AND ITS ENVIRONS
Growth Startups: Through the multiplier effect of the contributions of tech hubs in Minna, more startups have sprung up in figures across different entrepreneurial fields. An indication of how the employment of digital and technological innovations facilitates efficiency in creativity for problem-solving. This is also changing the mindset of the residents on possibilities of what they can achieve given the presence of tools for training and development provided by tech innovation hubs like JD Lab which seeks to target the educational sector by catching them young and grooming them as future creators, and accelerators.
Improvement in standard of living: The advent of tech hubs has helped raise the standard of living of the people in Minna through tech-driven processes to make day-to-day life activities easier and faster. Basic amenities made more accessible like the invention of prepaid water meters by Hamza Yunusa, CEO and founder of Hyrdronamics (MIT Bootcamp alum) which facilitates payment online is a quintessential example of how the impact of such creation is felt at the grassroots. JD Lab through its Innovation Hub, Labspace is working towards partnering with state governments and NGOs on how hubs can be used as a birthplace for innovative solutions to problems to improve the living standard of the people and economic growth of these Northern cities and states at large.
Investment: With the enabling environment created, one factor that drives local and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is the presence of tech hubs in a particular location. This is because it makes their investment more potent as their presence will help accelerate the progress of work in the environment. States or regions with the highest tech hubs tend to attract more FDIs and development than other places with little or no presence of them.
With the growing rise in startups supported under tech innovation hubs in Minna, the plight of the city is changing from a dearth of creative investment in the past to the depth of it in recent times.’
JD Lab through Labspace Nigeria provides spaces under its dynamic tech components that provide an enabling environment to attract foreign and local investment in the city of Minna and its environs. Serving as pre-incubator and accelerator to help facilitate startup ideas to fruition.
WORDS ON MARBLE
Tech Innovation Hubs are the engine to pilot any state or region or city towards prosperity in this digital economy age when technology is indispensable to growth and development. African countries need to adopt it into their schemes of blueprints for the future, starting from the present, in order to solve problems and stimulate local development to raise their standard of living.



















