Every developer knows the pain: you join a new team, open the codebase, and are immediately lost in a jungle of undocumented files. The authentication logic is split between auth-helper.js, user-validator.ts, and security-middleware.py. Payments are scattered across transaction-handler, billing-core, and checkout-utils. Onboarding takes weeks — not because the developer is slow, but because the system is impossible to navigate.
Ikponmwosa Marvelous Omorisiagbon, a Nigerian software engineer, has lived this struggle. So he built CodeLens AI — an open-source tool designed to make codebases as navigable as a well-documented system.
Why Onboarding Breaks Teams
Onboarding is one of the most expensive bottlenecks in software engineering. Teams lose productivity as new hires spend weeks asking senior developers where things live, or digging through thousands of lines of legacy code.
“In Africa, this problem is amplified,” Ikponmwosa told TechCabal. “Teams inherit code from contractors or previous developers. I’ve joined projects where it took weeks just to figure out how the login system worked.”
How CodeLens AI Works
CodeLens AI approaches the problem in two stages: structure and meaning.
- Indexing the codebase
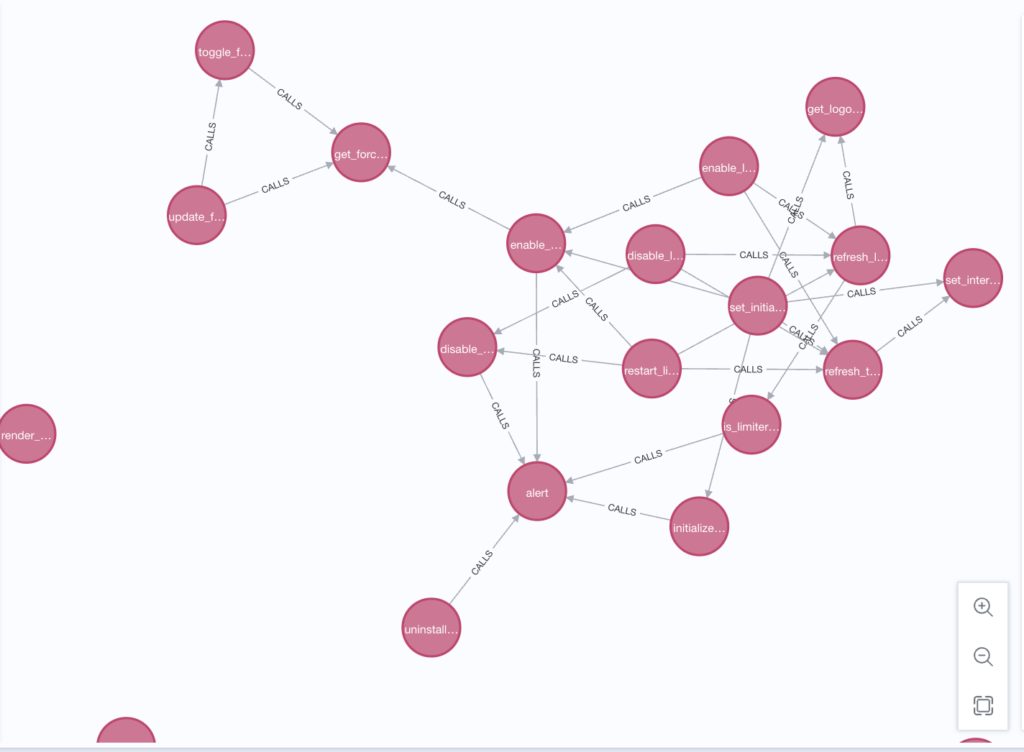
- It uses Tree-sitter AST and the Language Server Protocol (LSP) to parse code structure and capture deep relationships: which functions call each other, where definitions are made, and how files connect.
- This data is stored in a graph database, where nodes represent code elements and edges represent their interactions.
- It uses Tree-sitter AST and the Language Server Protocol (LSP) to parse code structure and capture deep relationships: which functions call each other, where definitions are made, and how files connect.
- Understanding the codebase
- Code blocks are then embedded into a vector database, which allows semantic search.
- An AI layer interprets these embeddings to provide conceptual answers — not just “where a function is written,” but what the code is actually doing.
- Code blocks are then embedded into a vector database, which allows semantic search.
Here’s what the graph looks like in practice:
Real Impact for Developers
- faster onboarding for developers joining complex projects.
- Automatic discovery of architecture patterns hidden in legacy systems.
- Semantic navigation that works even when documentation is missing or outdated.
Early Stage Innovation
CodeLens AI is still in its early development phase. It currently supports JavaScript, with TypeScript support in active development. Python and Java are next on the roadmap.
“We’re moving fast and iterating based on real developer feedback,” Ikponmwosa said. “New features are being rolled out quickly as we learn what developers actually need.”
By keeping the project open source, he hopes to attract contributors who can help refine and extend the tool.
The Problem Every Company Faces
Legacy systems power most of Africa’s fintechs, telcos, and enterprise platforms. Documentation rarely keeps up with the speed of growth, leaving new developers to guess how systems work.
CodeLens AI solves this by uncovering the implicit architecture hidden inside the code itself:
- Mapping system structure directly from the source.
- Spotting related functions scattered across files.
- Grouping tasks that belong to the same workflow.
“Legacy code stops being mysterious when you can ask it conceptual questions,” Ikponmwosa explained.
The Future of Code Understanding
As systems grow more complex and distributed teams become the norm, Ikponmwosa believes tools like CodeLens AI will become essential.
“Every codebase eventually becomes legacy code,” he said. “The question is whether we’ll keep struggling, or start building tools that make sense of it.”
For now, one Nigerian engineer has shipped a solution to a global problem — and it just might change how developers everywhere understand code.
Why Open Source Matters
Despite the commercial potential of developer productivity tools, Ikponmwosa made a deliberate choice to keep CodeLens AI completely open source.
“For me, it’s about giving back to the developer community,” he explained. “Every developer has struggled with understanding unfamiliar code. This shouldn’t be a privilege locked behind paywalls — it should be something anyone can use, improve, and build on.”
The project is available on GitHub, where developers are encouraged to use it freely, contribute improvements, and shape its future: https://github.com/marvikomo/code-lens-aI